Conclusion:
The conclusion is written at the end of the article along with the analysis of the June 21, 2020 Solar eclipse chart.
Analysis:
We are all going to witness Annular Solar Eclipse on June 21, 2020, which will be visible in India. There are several theories on effect of Solar and Lunar eclipse. As we are going to discuss about Solar eclipse, we will stick to effects of Solar eclipse. As per my experience, I have found the effect of Solar eclipse as follows;
- The effect of Solar eclipse is felt a month before the occurrence of the eclipse
- The effect remains throughout the year (from the date of eclipse) and can spill over to next year until the next eclipse or next year if the eclipse falls in the middle or end of the year.
- For the purpose of our analysis, we will take events unfolded in the year of eclipse and also the following year (if the Solar eclipse occurs in the 2nd half of the year).
- The effect is felt with respect to the house in which the eclipse falls with respect to stand alone eclipse chart.
- The effect is also felt with respect to the 2nd house, as the sign Gemini is the 2nd house of India Independence chart.
- The rising Ascendant at the time of eclipse and its placement with respect to India Independence chart.
- I have also attached with each Solar eclipse, the eclipse chart, and the world map showing whether it was visible in India. The effect of eclipse will be more intense when seen in the particular country. However, there is no correlation between visibility of the eclipse in a country and happening of the events. There have been eclipses in the past where it was not visible in India and yet we witnessed many major events.
- The closeness of Rahu/Ketu to eclipse point degree-wise is important. If Rahu/Ketu is in close conjunction to eclipse point then the effect is more malefic and intense.
- Similarly, closeness of Mars and Saturn also to the same eclipse degree. Its seen that when these malefics are retrograde and close to eclipse degree, then the malefic effect is more.
- Irrespective of the sign, any planet in the same degree as the eclipse degree is to be treated as conjunction. Therefore, when Jupiter is in the same degree as the eclipse degree, then Jupiter will give its protective cover. Similarly, when Mars or Sauturn are in same degree (it can be in any sign) to the eclipse degree, then the malefic effect of eclipse is seen more.
- In the chart given below, I have given the India Independence chart and the “Gochara (Transit)” chart refers to the planetary position at the time of Solar eclipse.
- All the major events are highlighted.
- I have from my worksheet, selected all those Solar eclipses those occurred in the sign Gemini from the year 1947 onwards.
June 30, 1954, 5.55.40 PM, Total Solar Eclipse. It was seen in India.


The events during the period 1954/55 are as follows: (source-Wikipedia)
- 22 March, 1954 – Jayendra Saraswathi becomes the 70th Shankaracharya of Kanchi.
- 5 July, 1954 – The Andhra Pradesh High Court is established.
- 11 August, 1954 – Indian annexation of Dadra and Nagar Haveli: Portuguese forces surrender to the Indian SRP.
- 6 November – Bombay Electricity Board is formed.
- 26 January – First Bharat Ratna in India.
- The Imperial Bank of India, the oldest (est. 1921) and the largest commercial bank of the Indian subcontinent, was transformed into the State Bank of India.
- The Hindu Marriage Act enacted
Comments – No negative events were felt as the Ascendant rising at the time of eclipse was the 7th house from the India Independence chart. The eclipse occurred in the 2nd house of the India chart. The 2nd house in the mundane chart signifies the wealth, banking, finance, treasury, etc. So, we witnessed transformation of Imperial Bank of India to State Bank of India. Since, Jupiter was also along with the eclipse point, spiritual, judiciary, etc events were witnessed like those in points no 1 and 2 above.
June 20, 1955, 9.41.44 am, Total Solar Eclipse. It was seen in India


The events during the period 1955/1956 are as follows: (source-Wikipedia). The events for 1955 have been covered in the previous eclipse above.
- 21 July, 1956– The 6.1 Ms Anjar earthquake shook Gujarat with a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (Violent), killing 115 and injuring 254.
- 1 September, 1956 – LIC of India began its Journey as a Pillar of Financial Backbone of India.
- 14 October, 1956 – Dr. B. R. Ambedkar, Indian Untouchable leader, converts to Buddhism along with 385,000 followers. See Neo-Buddhism.
- 1 November, 1956 – The States Reorganisation Act of India reformed the boundaries and names of Indian states.
- Exact date unknown – Gentlemen’s agreement of Andhra Pradesh (1956) signed
Comments: The eclipse falling in the 2nd house of India chart shows, establishment of LIC. The eclipse chart has exalted Jupiter in the Ascendant, we saw Dr. Ambedkar cult began. The eclipse occurred in the 12th house (losses) of the Solar eclipse chart, hence we witnessed earthquake in Gujarat. Eclipse is in close degree to Rahu/Ketu giving more malefic effect.
July 9, 1964, 5.00.46 pm, Partial Solar eclipse. Not visible in India.


The events during the period 1964/1965 are as follows: (source-Wikipedia).
- 27 May, 1964 – Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru dies after a five-month illness; he is succeeded by Lal Bahadur Shastri.
- 1964 – The Vishva Hindu Parishad is founded.
- 1964 – Hazratbal disappearance episode
- 1964 – The Seventeenth Amendment of the Constitution of India
- 1964 – IDBI Bank has established.
- 26 January, 1965 – Anti-Hindi agitations break out in India because of which Hindi does not get “National Language” status and remains one of the 23 Official Languages of India.
- 24 February, 1965 – English is adopted as an associate language in dealings between the Central government and the non Hindi speaking states.
- 20 March, 1965 – First fighting in the Indo-Pakistani War of 1965 between West Pakistan and India only.
- 29 May, 1965 Dhanbad coal mine disaster – A mining accident in Dhanbad, India kills 274.
- 5 August, 1965 – War begins between India and Pakistan.
- 2 September, 1965 – Kashmir is declared an “Integral Part of India” and is not a “disputed territory”, later responded by the Pakistani troops entering the Indian sector of Kashmir.
- 6 September, 1965 – Indian troops attempt to invade Lahore.
- 6 September – 22 September, 1965 – A full-scale Indo-Pakistani war is fought over Kashmir, which ends after a UN Security Council calls for a ceasefire on 20 September.
- 8 September, 1965 – India opens two additional fronts against Pakistan.
- 9 September, 1965 – U.N. Secretary General U Thant negotiates with Pakistan President Ayub Khan.
- 16 September, 1965 – China protests against Indian provocations in its border region.
- 18 September, 1965 – Soviet Premier Alexei Kosygin invites the leaders of India and Pakistan to meet in the Soviet Union to negotiate.
- 22 September, 1965 – Radio Peking announces that Indian troops have dismantled their equipment on the Chinese side of the border.
- 24 September, 1965 – Fighting resumes between Indian and Pakistani troops.
- 1 December, 1965 – The Border Security Force is formed as a special force to guard the borders.
Comments: The solar eclipse Ascendant is falling in sign Scorpio, which is the 7th house of the India chart, which signifies war. The 7th house of the eclipse chart has Mars. This Mars is in the same degree as the eclipse point and hence giving the malefic effect of Mars. Therefore the 7th house effect of war was witnessed in the subsequent year in 1965. In the eclipse chart, the Ascendant rising is Scorpio and the 10th house (Government, famous personalities, leaders, etc) lord Sun is in the 8th house (death). We saw, Nehru died. Again the IDBI Bank got established due to the eclipse falling in the 2nd house of India chart, signifying wealth, treasury, banking, etc.
July 11, 1972, 1.08.45 am, Total Solar eclipse. Not visible in India.


The events during the period 1972/1973 are as follows: (source-Wikipedia).
- 2 July, 1972 – Following Pakistan’s surrender to India in the Indo-Pakistani War of 1971, both nations sign the historic bilateral Simla Agreement, agreeing to settle their disputes peacefully.
- 10 July, 1972 – A stampede of elephants kills 24 people in the Chandka Forest.
- Armed Forces (Assam and Manipur) Special Powers (Amendment) Act, 1972
- 15 August 1972 Pincode (postal index Number- PIN) Introduced in India
- 9 September 1972 wild life protection Act.
- 1 April, 1973 – Government campaign to save the tiger from extinction.
Comments: The Solar eclipse Ascendant is in the sign Aries, ehich is the 12th house of the India chart. The eclipse in Gemini gets the benefic aspect of Jupiter from Sagittarius. Due, to this no negative events occurred. The eclipse chart had Aries sign rising and eclipse in the 3rd house (communications) in the sign Gemini. The sign Gemini signifies all forms of communications including Post and telegraph, hence the event of PIN code introduction was witnessed. So, Jupiter’s aspect is a saving grace as is seen in the previous charts too.
June 30, 1973, 5.08.44 pm, Total Solar eclipse. Partially visible in India.


The events during the period 1973/1974 are as follows: (source-Wikipedia). The events for 1973 is given under previous Solar eclipse. The events for 1974 are as follows;
- December 1973 – March 1974 – Navnirman Andolan (Re-construction movement) was a socio-political movement in 1974 in Gujarat by students and middle-class against economic crisis and corruption in public life. It resulted in dissolution of the elected government of the state at that time.
- January – April, 1974 – Worli riots refers to the violence that occurred in the chawl in the Worli neighborhood of Mumbai between January and April 1974.
- January – May, 1974 – smallpox epidemic
- March 1974 – June 1975 – Bihar Movement was a movement initiated by students in Bihar in 1974 and led by the veteran Gandhian socialist Jayaprakash Narayan, against misrule and corruption in the Government of Bihar.
- 18 May, 1974 – Under project Smiling Buddha, India successfully detonates its first nuclear weapon in the Thar Desert, and becomes the sixth nation to do so.
- May – 1974 railway strike in India was a major strike by the workers of Indian Railways. The strike lasted from 8 to 27 May 1974. The 20 day strike by 1.7 million workers is the largest recorded industrial action in the world.
Comments: The Ascendant of the eclipse chart in the sign Scorpio, which falls in the 7th house of the India chart. No benefic aspect of Jupiter. Infact, Jupiter is debilitated. The Nodes are very close to eclipse degrees, hence its malefic effect. The Ascendant degree of eclipse is also almost of the same degree as the eclipse degree. The eclipse occurs in the 8th house of the eclipse chart. The 8th house is epidemic/pandemic. We witnessed the events like riots, mass movements, small pox epidemics, etc. The strike by Railways is due to the eclipse forming in the sign Gemini, the sign of communications.
June 20, 1974, 10.25.39 am, Total Solar eclipse. Not visible in India.


The events during the period 1974/1975 are as follows: (source-Wikipedia). The events for 1974 is given under previous Solar eclipse. The events for 1975 are as follows;
- 19 January, 1975 – The 6.8 Ms Kinnaur earthquake shook northern India with a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (Violent). Forty-seven people were killed.
- 19 April, 1975 – The first Indian satellite, Aryabhata, goes into Earth’s orbit.
- 16 May, 1975 – Sikkim annexed to India after a deposing the monarchy.
- 25 June, 1975 – A state of emergency is declared by Prime Minister Indira Gandhi during which the press is censored and 100,000 are jailed.
- Chasnala mining disaster
Comments: The Ascendant of the eclipse falls in the sign Leo, which is the 4th house of the India chart signifying Opposition parties. The Ascendant degree is also same as the eclipse degrees. The lord of 4th house (Ascendant of eclipse chart) is Sun and its eclipsed. The 4th house is also the house of natural calamities. The aspect of Jupiter is of no use, as it is in exact kendra to Nodes. So, Jupiter loses its power. The 4th lord of the eclipse chart, Mars is debilitated in the 12th house. Therefore, we witnessed events like earthquake, and state of emergency declaration (where the opposition leaders were jailed during emergency). The launching of satellite is due to the sign Gemini, which represents all forms of communications.
June 21, 1982, 5.21.45 pm, Partial Solar eclipse. Not visible in India.


The events during the period 1982/1983 are as follows: (source-Wikipedia).
- July, 1982 – NABARD establishment
- February, 1983 – Bandit queen Phoolan Devi surrenders.
- 18 February, 1983 – Nellie massacre: over 2,000 people, mostly Bangladeshi Muslims, were massacred during the Assam agitation.
Comments: The eclipse Ascendant occurs in the sign Scorpio, which is the 7th house of the India chart. There is an aspect of Jupiter on the eclipse in Gemini. The Jupiter is also in the same degree as the eclipse degrees. The eclipse falls in the 2nd house of the India chart, signifying treasury, banking, etc. Hence, the establishment of banking institution NABARD. One of event of Nellie massacre occurred.
July 12, 1991, 12.36.05 am, Total Solar Eclipse. Not visible in India.


The events during the period 1991/1992 are as follows: (source-Wikipedia).
- 15 June, 1991 – When the general election results are all compiled, the Congress Party has won a plurality of votes.
- 21 June, 1991 – Indian National Congress leader P.V. Narasimha Rao becomes Prime Minister.
- 24 June, 1991 – J. Jayalalithaa is sworn in as chief minister of Tamil Nadu for the first time.
- 24 July, 1991 – The government of India announces its New Industrial Policy, marking the start of India’s economic reforms.
- 11 October, 1991 – Sikh separatists bomb a Hindu procession in Lucknow, killing 41 people.
- 20 October, 1991 – The 6.8 Mw Uttarkashi earthquake shook northern India with a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (Violent), killing 768–2,000 and injuring 1,383–1,800.
- 11 December, 1991 – Rapid Action Force established by Union Home Ministry.
- 1 February, 1992 – Chief Judicial Magistrate of Bhopal Court declares Warren Anderson, ex-CEO of Union Carbide, a fugitive under Indian law for failing to appear in the Bhopal disaster case, and orders the Indian government to press for an extradition from the United States.
- May, 1992 – Over 200 people die in Cuttack in Odisha, after drinking illegally brewed liquor. About 600 people were hospitalised (see: 1992 Odisha liquor deaths).
Comments: The Ascendant rising in the eclipse chart is Pisces, which is the 11th house of India chart. Its in Gandanth (a dangerous gandanth between watery and fiery sign). The eclipse falls in the 4th house of the eclipse chart. The 4th house signifies natural calamities. Therefore, we witnessed earthquake taking away lives of people. The planet Jupiter is exalted in the eclipse chart, but in D9 of the eclipse chart its debilitated. Also, Rahu/Ketu is in degreecal conjunction with Sun/Moon, showing the gravity of the situation. Just before the eclipse in July 1991, in the month of May 1991, Rajiv Gandhi was assassinated.
June 30, 1992, 5.48.01 pm, Total Solar Eclipse. Not visible in India.
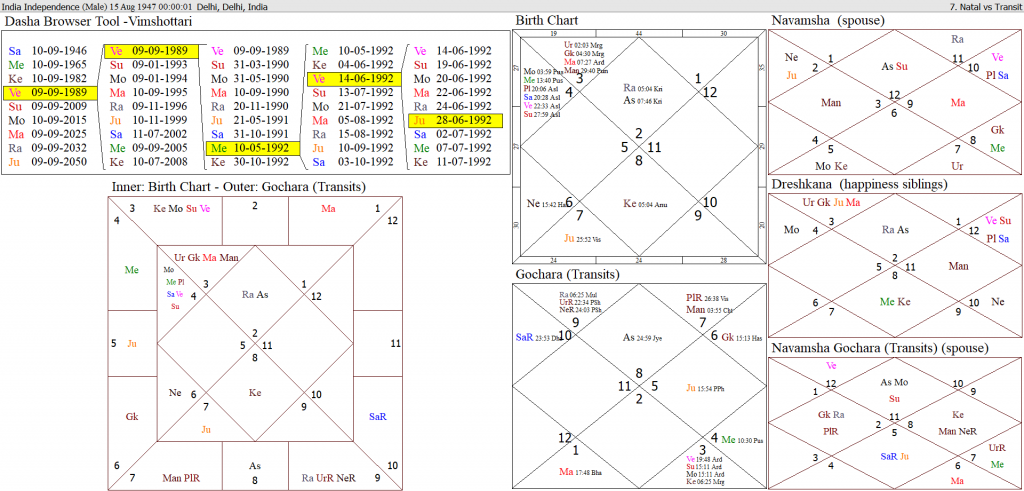

The events during the period 1992/1993 are as follows: (source-Wikipedia).
- May, 1992 – Over 200 people die in Cuttack in Odisha, after drinking illegally brewed liquor. About 600 people were hospitalised (see: 1992 Odisha liquor deaths).
- 14 August, 1992 – Veerappan Gang Trapped and killed Mysore District SP, T.Harikrishna, SI Shakeel Ahmed and four constables named Benegonda, C.M.Kalappa, Sundara and M.P.Appachu, through a false informant near Meenyam in Karnataka
- 2 October, 1992 – Zee Television, a Hindi language satellite and cable television station, a first officially regular broadcasting service to start in Mumbai.[1]
- 6 December, 1992 – Members of the Vishva Hindu Parishad (VHP, World Hindu Council) tear down a 16th-century mosque located in Ayodhya, in Northern India. The mosque is built over a shrine which exhorted the small piece of land as Ram Janmabhoomi – the birthplace of Lord Rama. This sparks off nationwide communal riots in which some 3,000 people die.
- 1992 – Government of India establishes SEBI, stock exchange regulator.
- 1992 – Indian Rupee exchange rate collapsed. It was 20 Rs to 1 dollar in January 1992 and it became 30 Rs to 1 dollar in December 1992. A huge 50% depreciation in value.
- 9 March, 1993 – The All Parties Hurriyat Conference is formed in Kashmir.
- 12 March, 1993 – A series of bomb blasts, thought to be planted by underworld figures, rock the country’s commercial capital of Bombay, killing some 260 people. (See 1993 Mumbai bombings.)
- 9 April, 1993 – Veerappan Gang Trapped and blew a Tamil Nadu bus carrying police, forest officials and civilians, using a landmine, which killed 22 civilians and police and this incident is known as Palar blast.
- 14 April, 1993 – Sun TV, a Tamil language television station, as first regular broadcasting service to start in Chennai, Tamil Nadu.
- 24 May, 1993 : Veerappan and His gang Killed 6 policemen K.M.Uthappa, Prabhakara, Poovaiah, Machaiah, Swamy and Narasappa of STF commander Gopal Hosur’s party and injured the police commander near Rangaswamy vaddu, M.M.Hills, Karnataka.
- 30 September, 1993 – The 6.2 Mw Latur earthquake shakes Maharashtra, India with a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe) killing 9,748 and injuring 30,000.
- 1993 – Mulayam Singh Yadav elected chief minister of Uttar Pradesh for the second time.
Comments: The Ascendant rising in the eclipse chart is Scorpio, the 7th house of India chart. The eclipse occurs in the 8th house of the eclipse chart. The 6th, 8th and 12th houses are not good houses for any planet to be in, except that when its aspected by benefics. The 8th house is mass happenings, hence, we witnessed Babri masjid demolition of a mass scale. If you have noticed, in the eclipse chart, the planet Jupiter is at 15 deg 54 of Leo. The degree of eclipse is also at the same degree in Gemini. This is known in astrology as “Disjoint Degreecal conjunction”. Since, Jupiter was afflicted degreecally by the eclipse point, we saw the mass scale movement of Babri Masjid demolition. Jupiter also signifies communalism, religion, fanaticism, etc. The 2nd house (treasury, finance, banking, etc.) of eclipse chart is Jupiter and the 11th house (income, fdi, fiscal deficit, etc) of India chart is also Jupiter. As we have seen Jupiter is afflicted for the reasons mentioned above. Due to this we saw Indian Rupee collapsed. Mars is in the 6th house very strong in its own house and aspecting the 8th lord Mercury. Mars is also close to the degree of the eclipse (we can take orb of 2 to 3 degree). The 6th house Mars is bomb blasts, terror attacks, etc. Hence, we witnessed many mass happenings like earthquakes, serial bomb blasts, etc. Further, Mars is in the kendra to Saturn (the 4th lord of eclipse chart, signifying natural calamities). Kendra effect is supposed to give a strong effect as per the rules of Parashara.
July 2, 2000, 12.49.55 am, Partial Solar eclipse. Not visible in India.


The events during the period 2000/2001 are as follows: (source-Wikipedia).
June, 2000.
- 1 June – 2000 – Pen Power, an Encyclopedia of published letters to the editors from some 200 letter writers was released by M.V.Kamath, Chairperson of Prasar Bharati. The veteran journalist declares that Pen-Power should be prescribed as a text book in all Journalism colleges.
- Early June – Clashes between security forces and terrorists in Jammu and Kashmir kill 17 people. Violence in the region has become a daily occurrence as it also has in the far-eastern state of Tripura where killings of Bengalis by Christian separatist rebels have prompted the deployment of an extra 3,000 paramilitary troops by the government.
- Mid-June – Prime Minister Vajpayee approves a measure to provide 320,000 government employees with free telephones. India has only 26 phone lines per 1,000 people.
- 11 June – Rajesh Pilot, a senior member of the opposition Congress party, dies in a car crash. Hundreds of supporters mourn outside the home of the popular politician who, analysts say, was an important figure of stability within the party and a likely successor to Congress leader Sonia Gandhi.
- Mid-June – Reliance Industries, the country’s biggest private company, announces plans to enter into the information technology industry. A new subsidiary, Reliance Infocomm, will oversee the laying of fibre-optic cables to connect the top 115 cities to the Internet.
- Mid-June – London-based human rights group Amnesty International criticizes India, along with Bangladesh and Pakistan, for insufficiently protecting the rights of women, who, it says, are subjected to negative bias in investigations of abuse.
- 16 June – 34 lower-caste Hindus are killed in the northeastern state of Bihar; eight suspects are arrested two days later. The massacre was believed to be a revenge killing for 12 upper-caste Hindus who were killed a week before. The banned private army Ranvir Sena was believed to have been responsible for the latest killing and for 350 other deaths since 1994.
- Mid-June – Archaeologists announce a significant discovery of treasure believed to be around 5,000 years old in the northern state of Uttar Pradesh. The jewelry was thought to belong to a civilization from the Indus Valley not previously thought to have spread so far afield.
- Late June – The government announces plans to subsidize health insurance for the “poorest of the poor”.
- Late June – Eight executives from the independent television station Channel V are arrested and charged with obscenity and indecency after screening a program in which two teenage girls were encouraged to strip on the streets of Mumbai for a small cash incentive.
- 24 June – Almost 1 billion people worldwide reportedly tune in to watch the International Indian Film Awards held at the Millennium Dome in London, England. The Indian film industry, known as Bollywood, has its second-largest following in the UK, mostly amongst the country’s ethnic Indian population, but receives little attention from the British press.
- 26 June – The state assembly of Jammu and Kashmir angers the federal government when it resolves to ask for a return of the region’s autonomous status which was revoked in 1953. The government refuses to discuss the proposal in parliament in early July and rejects the calls outright.
- 27 June – The Supreme Court calls on the government to review its list of employees and remove “the indolent, infirm, and those of doubtful integrity, reputation, or utility”.
- 28 June – India joins a select group of six countries when it commences regular summits with the European Union. The other five countries which have regular consultations with the EU are Canada, China, Japan, Russia and the U.S..
July, 2000
- Early July – The first passenger rail link between India and Bangladesh in 26 years was opened. The line between Benapole in Bangladesh and Petrapole in West Bengal was closed due to lack of commercial interest in 1974.
- Early July – Wildlife experts announce an investigation into the mysterious sudden deaths of 12 of the 56 rare Royal Bengal tigers in Nandankanan Zoo in Orissa. There are thought to be fewer than 4,000 tigers in the wild in India.
- Mid-July – The UN’s Population Fund condemns the government for its lack of commitment to tackle the imbalance between numbers of males and females in the country which it was thought was largely due to the feticide and infanticide of baby girls. There are estimated to be 960 women to every 1,000 men.
- Mid-July – A landslide in Mumbai’s slum district kills at least 60 people after torrential rain. A further 200 people are feared lost under the rubble.
- 15 July – Prime Minister Vajpayee announces that long-distance domestic phone lines will be fully deregulated from 15 August to help boost the country’s information technology industry.
- 17 July – More than 50 people are killed when a Boeing 737 passenger plane crashes in a residential area of Patna.
- July – Authorities in Sikkim uphold complaints from local Buddhists and ban expeditions up the northeast face of the world’s third highest mountain peak, Kanchenjunga, which was revered by local people as a deity.
- 22 July – The government announces the launch of a National Population Stabilization Fund to help promote family planning programs in the country, especially in the northern states which contain half of all Indians. The population officially passed the 1 billion mark on 11 May, although the UN believes that figure had already been reached on 15 August 1999.
- 23 July – Minister for Law Ram Jethmalani resigns from the cabinet blaming strained relations with Attorney General Soli Sorabjee.
- Late July – Bal Thackeray, leader of the far-right Shiv Sena group, was released within hours of his arrest. The court claims that too much time has passed since his alleged crimes of promoting “communal enmity” to warrant prosecution. The Maharashtra state government, whose decision to press the charges had prompted threats from Shiv Sena supporters to disrupt commerce in Mumbai, says it will appeal against the ruling.
- Late July – Thousands of police officers in the crime-plagued eastern state of Bihar go on strike to demand better compensation for the families of fallen comrades, and less “political interference” in their work.
- Late July – 10,000 homes are destroyed and 40 people killed in severe flooding in the northwestern state of Rajasthan.
- 24 July – The government’s commitment to privatization plans was confirmed with the naming of ex-journalist and committed free-market economist Arun Shourie as minister for privatization.
- Late July – The government and separatist rebels from the far-eastern border state of Nagaland agree to extend their ceasefire for a further year in an attempt to bring a lasting solution to the 53-year rebellion.
- 30 July – The Indian film idol Rajkumar was part of a group taken hostage by a notorious Karnataka bandit known as Veerappan. A popular outcry places the state government under strong pressure to negotiate Rajkumar’s release, but in August the Supreme Court rules out a deal involving the release of imprisoned members of Veerappan’s elephant poaching and timber smuggling band. One of Rajkumar’s fellow hostages manages to escape from his captors on 28 September.
August, 2000
- 1 August – Bangaru Laxman, a junior minister in the cabinet, was appointed as the new president of the ruling BJP. Laxman was the first lower-caste Hindu and southern Indian to hold the position and says he will look to expand the party’s support base in the south. As a known moderate it was thought he will also seek to mend strained relations with the Hindu right.
- Early August – Around 90 Hindus are massacred by Muslim separatists in Indian-administered Kashmir. The violence was thought to be a hostile reaction to peace initiatives begun by the largest separatist group Hizbul Mujahideen.
- Early August – Five people suspected of being witches are burned alive by 200 angry villagers in the southern state of Andhra Pradesh. Almost all of the village’s 1,500 inhabitants flee their homes after the crime.
- Early August – Severe rainfall over the Himalayas causes widespread devastation across northern and eastern areas of the country. More than 100 people are killed and over 5 million made homeless in the states of Himachal Pradesh, West Bengal, and Assam.
- Early August – Thousands of women demonstrate in New Delhi in support of the government’s proposed “reservations bill” which will guarantee women one-third of all parliamentary seats. Pressure groups note that despite the prime minister’s promises the bill has not been listed on the current parliamentary schedule.
- 8 August – A ceasefire initiated on 24 July between the government and the Kashmiri separatist group Hizbul Mujahideen falls apart after only 15 days after accusations that the government has fired on some of the group’s members. Prime Minister Vajpayee urges that his government was still prepared to discuss peace initiatives but states that any deal will have to be worked out within the framework of the Indian constitution, which Hizbul Mujahideen has flatly rejected as a basis for peace. The government also refuses to address the group’s key demand that Pakistan be involved in any talks.
- Late August – The regionalist debate was invigorated by government proposals to share out the revenue of the various states. Delegates from ten states meet with the prime minister to urge him to drop the proposals. They claim the policy will penalize states which have managed to increase revenue through hard-won reforms.
- Late August – Over 100 people die in severe monsoon rains in southern India. In the face of the torrential downpour more than 50,000 people are evacuated, mostly from Hyderabad which receives over half of its average annual rainfall in 24 hours.
- 24 August – The army claims it has killed at least ten Pakistani soldiers after attacking around 40 troops attempting to penetrate Indian territory. It was the worst cross-border incident since an unofficial ceasefire was agreed in June.
September, 2000
- 6 September – 300,000 telecom workers begin an indefinite strike to protest against the government’s decision to transform the department of telecommunications into a state-run corporation.
- Early September – The onslaught against overpopulation continues in the western state of Maharashtra when the state’s government decides to withhold benefits from May 2001 for families with more than two children. A two-child maximum was already a prerequisite for employment by the state, and the authorities are also considering enforcing a law to prevent women from marrying under the age of 18.
- Mid-September – The environmentalist group Greenpeace criticizes the government for not doing enough to enforce regulations banning the dumping of international toxic waste in India.
- Mid-September – The World Health Organization (WHO) warns that 1 billion people worldwide are regularly exposed to levels of air pollution 100 times greater than recommended guidelines. The greatest risk was from the use of solid fuel in poor households, rather than from industrial smog in large cities. It notes that 500,000 children from rural areas die every year from respiratory infections in India where 80% of homes use solid fuel for cooking and heating.
- September – On average in India 24 women are raped every day and 14 killed to “protect their family’s honour” according to the UN’s latest State of the World’s Population report. It also reveals that 40% of Indian women are subjected to domestic violence.
- Late September – India and South Africa sign a defense cooperation agreement in Cape Town covering peacekeeping, weapons development and procurement, and counter-terrorism. South Africa hopes that India’s experience in peacekeeping can be applied in conflict resolution in southern Africa.
- 29 September – Newspapers hail the conviction of former prime minister P.V. Narasimha Rao as a landmark moment in Indian law. He was found guilty of corruption in a bribery scandal dating from 1993 and the decision was interpreted by the press as a clear signal that high rank does not provide legal protection.
- End of September – Flooding in eastern states has left many millions homeless and has killed 850 people in the state of West Bengal alone.
- 30 September – The Communist Party of India – Marxist (CPI-M), the third largest party at federal level, has its status as a “national” party revoked by the electoral commission. The move was a serious threat to the party which controls two states outright, including the populous state of West Bengal, and was the leading coalition partner in another.
October, 2000
- Early October – A senior Hindu leader urges the government to establish a national Christian church and expel foreign missionaries. The country’s Christian community was often subject to violent intimidation from extremist Hindu activists.
- 3 October – Prime Minister Vajpayee signs a bilateral agreement with Russian President Vladimir Putin to increase ties between the two countries including cooperation on issues of defense.
- Mid-October – The Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE) revises its predictions, lowering the forecast rate of economic growth for 2000 from 7% to 5.8%.
- Mid-October – The Information Technology Act 2000 comes into force providing regulations for e-commerce and punishment for improper use of the Internet. Digital signatures are now legal, and distributors of cyber pornography can face up to five years imprisonment. The act includes a controversial clause allowing police to make searches and arrest suspects in public places without a warrant.
- Mid-October – The chief minister of the northeastern state of Arunachal Pradesh complains that Chinese soldiers are making regular forays across the agreed Line of Actual Control to harass villagers. The Chinese government dismisses the claims as inaccurate.
- Mid-October – A court in the western state of Gujarat rules in favour of the vertical extension of the controversial Sardar Sarovar dam on the River Narmada. Work on the dam was halted in 1994 due to strong local objections. Supporters of the project point to the beneficial effects of more water for the drought-plagued region and an increase in hydroelectric power while opponents argue that the subsequent displacement of thousands of villagers around the river was insupportable.
November, 2000
- 1 November – Chhattisgarh, carved out of Madhya Pradesh, becomes India’s 26th state.
- 6 November – Buddhadeb Bhattacharjee was sworn in as the new chief minister of West Bengal following the retirement of Jyoti Basu, the world’s longest-serving elected communist leader.
- 9 November – Uttaranchal, now known as Uttarakhand, carved out of Uttar Pradesh, becomes India’s 27th state.
- Early November – Syed Salahuddin, leader of the Kashmiri separatist group Hizbul Mujahideen, calls on Muslim nations to cut ties with India and says the group will not renew a unilateral ceasefire. It calls for the Indian government to officially recognize that Jammu and Kashmir was a disputed territory and for any further negotiations to include the Pakistani government and the people of Kashmir.
- Mid-November – Three months of extreme embarrassment for the state governments of Tamil Nadu and Karnataka end when the notorious aging bandit Veerappan suddenly releases an even older veteran actor, Rajkumar, he had held captive since August. The authorities, keenly aware of the popularity of Rajkumar, agreed in August to grant some of Veerappan’s demands which included the official recognition of Tamil as a language used in business in Karnataka, and the release of prisoners held under strict anti-terrorist laws. It remains unclear what exactly prompted the release of Rajkumar.
- 15 November – Sonia Gandhi easily wins reelection as leader of the Congress (I) party, beating Jitendra Prasada by 7,448 votes to 94. Prasada was the first person to challenge a member of the Nehru-Gandhi dynasty which has dominated Congress since the 1950s.
- 15 November – Jharkhand, carved out of Bihar, becomes India’s 28th state.
- Late November – Violent protests force the government to rethink plans to close heavily polluting industries in Delhi. Workers from the doomed factories clash with police while demonstrating against the environmentally motivated decision which would lead to job losses.
- Late November – Ten people, including three Indian soldiers, are killed in a landmine attack in Kashmir on the first day of a government ceasefire held to coincide with the Muslim holy month of Ramadan. The terrorist group Hizbul Mujahideen claim responsibility for the attack condemning the ceasefire as a publicity stunt intended to win over international opinion.
- Late November – India’s chief corruption commissioner N. Vittal declares that the country’s entire political system depends on illegal funding.
December, 2000
- 1 December – Miss India first runner-up Priyanka Chopra wins the Miss World 2000 title.
- 2 December – Pakistan offers to exercise “maximum restraint” in contested border areas of Kashmir as a beginning to negotiations with the Indian authorities. India insists that before there can be talks there must be a complete cessation of firing across the Line of Control.
- Early December – Political turmoil was ignited by the anniversary of the destruction of a mosque by Hindu extremists at Ayodhya, Uttar Pradesh, in 1992. It leads to calls for the resignation of Prime Minister Vajpayee and leaves the lower house of parliament, the Lok Sabha, in stalemate. Vajpayee suggests that the construction of a Hindu temple on the site of the mosque, reputedly the birthplace of a Hindu deity, was “an expression of national yearning”.
- 17 December – An alliance of Kashmiri separatists, the Hurriyat, begin talks to discuss a unified response to the Indian government’s ceasefire but divisions between the factions drag the conference into a second day.
- 20 December – In response to the Indian government’s extension of its unilateral ceasefire in Kashmir for a further month, the Pakistani authorities announce that they will partially withdraw troops from the disputed line of control.
- Late December – Relations with Pakistan are damaged when Prime Minister Vajpayee accuses the Pakistani authorities of being behind threats made by the extremist Kashmiri separatist group Lashkar-e-Toiba against his own person. The group, which was based in Pakistan, launched a surprise attack on the historic Red Fort in Delhi on 22 December, killing three people and undermining Vajpayee’s Ramadan ceasefire, which had been extended for an extra month two days earlier.
January, 2001
- 1 January – Calcutta officially becomes Kolkata, reverting to its precolonial name.
- 1 January Dr. Leo Rebello’s Encyclopedia of Letters Pen Power and All India Letter Writers Association is entered as a World Record in the Limca Book of Records.
- 2 January – Power cuts leave huge swathes of northern India in darkness for two days starting early on 2 January. A minor fault in Uttar Pradesh leads to a breakdown in the regional grid across Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Kashmir, Punjab, and Rajasthan.
- Early January – The government announces that it aims to double the number of aircraft operated by Air India in the next five to seven years as well as to sell off a 60% share in the company. Air India’s stock of aging craft is thought to have dulled the company’s competitive edge in recent years.
- Early January – The president of the Indian Science Congress, R.S. Paroda, warns a conference of 3,000 Indian scientists that the country could face a severe food shortage in 2020 as the population size outstrips the country’s level of supplies.
- 4 January – The government tests its first homemade jet fighter, the Light Combat Aircraft (LCA). The plane, originally scheduled to take its maiden flight in 1991, has taken 17 years to develop and will not be ready for service until 2010.
- 9 January-21 February – More than 100 million people – almost 2% of the world’s population – attend the Maha Kumbh Mela festival in Allahabad, making it the largest gathering of human beings in history. On the festival’s most important day an estimated 20 million Hindu pilgrims bathe in the sacred waters of the three rivers which meet near the town. The festival is held every 12 years.
- 15 January – Voters in Indian-administered Kashmir are able to participate in the first local elections in 23 years. The polls decide positions on some 125 village councils. Islamic militants have urged a boycott of the vote, which they say will undermine the separatist movement.
- 15 January – In a sign of improving relations, Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee meets with the visiting chairman of China’s National People’s Congress, Li Peng. Both leaders say they have made substantial progress in discussing their two countries’ disputed borders.
- 16 January- 11 people are killed when six members of the Kashmiri separatist guerrilla group Lashkar-e-Toiba attempt to storm Srinagar’s civilian airport.
- Mid-January – The government announces that it is willing to meet the United Liberation Front of Assam (ULFA) for open negotiations on ending the 20-year insurgency in the northeastern state.
- Mid-January – The eastern state of Orissa urges further government assistance in the face of a major drought. Officials estimate that the state has lost around $150.7 million in failed rice crops alone. It is thought that deforestation has played a major part in the drought.
- 17 January – Pakistan reacts angrily to news that the Indian military has successfully test-fired an improved Agni-II intermediate ballistic missile capable of carrying a nuclear warhead to anywhere in Pakistan.
- Mid-January – Researchers reveal that unusually high sea temperatures caused by the extreme weather effect known as El Niño have irreversibly damaged coral reefs off India’s western coast.
- Late January – 150 million children across India are immunized against polio in one of the largest vaccination projects ever undertaken.
- Late January – The government extends its ceasefire in Kashmir for another month despite continuing separatist violence.
- 26 January – The 7.7 Mw Gujarat earthquake shakes Western India with a maximum Mercalli intensity of X (Extreme), leaving 13,805–20,023 dead and about 166,800 injured.
- Late January – The UK-based human rights group Amnesty International urges the government to crack down on the widespread use of torture by police.
- Late January- Researchers in Bangalore announce that the common antibiotic Triclosan has significant effects against the malaria parasite. Malaria is thought to kill around 1 million people every year worldwide.
February, 2001
- Early February – Authorities and aid workers in Gujarat warn that disease is now the biggest problem threatening the 1 million people made homeless by the January earthquake. Fears of a major epidemic are increased as the thousands of corpses still trapped beneath fallen buildings begin to decompose.
- Early February – The government grants refugee status to Ogyen Trinley Dorje, a controversial claimant to the 17th Karmapa title. The Karmapa was in India since escaping Tibet in early 2000.
- 2 February – An unprecedented telephone conversation between Prime Minister Vajpayee and Pakistani military leader General Pervez Musharraf is hailed as a major step in relations between the two countries. Musharraf contacts his Indian counterpart to offer further emergency aid for the survivors of the Gujarat earthquake.
- Early February – The drug manufacturer Cipla, based in Mumbai, announces that it plans to offer anti-AIDS drugs at very low prices. The three-drug cocktail used to help AIDS victims currently costs around $12,000 per patient per year. Cipla says it will offer a three-tier pricing structure with wholesalers paying $1,200, governments $600, and the French charity Médecins sans Frontières just $350 per patient per year.
- Mid-February – In a sign of thawing relations, Foreign Minister Jaswant Singh begins an official visit to Myanmar. He is the first Indian minister to go to the country since the military junta came to power there in 1988.
- Mid-February – Violent protests by Kashmiri separatists in Srinagar intensify. Five Indian policemen are killed on 19 February alone in riots sparked by the death of four stone-throwing demonstrators killed by police in Haigam, 40 km north of Srinagar, four days earlier.
- Late February – The government extends its ceasefire in separatist Kashmir for an extra three months.
- Late February – A unilateral 15-day ceasefire is declared by the government in the far northeastern separatist state of Manipur. The cessation of hostilities will begin on 1 March to coincide with the start of the local Yaosang festival.
March, 2001
- 15 March – Defense Minister George Fernandes resigns in a bribery scandal which threatens to bring down the government. The leader of the ruling Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), Bangaru Laxman, has already left his position, but the departures fail to calm opposition parties, who continue to stall the workings of parliament for a third day on 16 March. Journalists released secretly filmed footage on the Internet, showing government members from the defense ministry and other senior figures accepting bribes from bogus arms dealers.
- 28 March – A counter-insurgency Special Operations Group (SOG) patrol claims to have killed Salaudin Ayubi, the Pakistani-based Lashkar-e-Toiba’s leader in the Kashmir valley, in a shootout near Srinagar. There has been a spate of attacks by militants in Srinagar in recent months, although the ceasefire announced by the Indian government in November remains nominally in place.
- Late March – Provisional results of the 2001 census are released, providing official confirmation that the country’s population now exceeds one billion. The full census results are not expected until 2003.
April, 2001
- Beginning of April – Widespread strike action by private owners of buses, taxis, and motorized rickshaws contributes to chaotic traffic conditions in Delhi, as new rules come into force requiring a switch from diesel fuel to compressed natural gas in a bid to combat urban air pollution.
- Early April – Customs and excise chief B.P. Verma is arrested on charges of corruption.
- 2 April-4 April – A conference in Delhi, organized under the UN Environment Programme’s Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES), brings together for the first time the members of a new task force on the future of tigers in the wild – thought to number 5,000–7,000 in total.
- Early April – In a bold attempt to hasten an end to violence in separatist Kashmir, the government offers unconditional peace talks to Kashmiri militants. However, with no invitation to the Pakistani authorities it is not likely to attract much response from the separatists.
- Early April – The Tibetan spiritual leader, the 14th Dalai Lama Tenzin Gyatso, welcomes news that tens of thousands of Dalits (lower-caste Hindus) are to convert to Buddhism on 14 October.
- Early April – Tea production in the northeastern region of Darjeeling is adversely affected by an indefinite general strike called by the Gorkha National Liberation Front (GNLF) over the government’s failure to identify the perpetrators of an attack on their leader, Subhas Ghising.
- Mid-April – Extra troops are dispatched to the Bangladeshi border after 18 soldiers are killed in escalating shooting incidents. Tension in the region has mounted over a disputed section of the border south of Assam.
- Mid-April – Opposition parties recommence the disruption of parliament in an attempt to force the government to launch an investigation into an allegedly corrupt arms deal.
- 18 April – The country’s space program is brought into a new era with the successful test launch of its geostationary satellite launch vehicle, the GSLV-D1, at Sriharikota in Andhra Pradesh. The program had caused embarrassment for the country’s space agency in late March when the first test launch, broadcast live on television, was aborted as flames burst from the craft on ignition. Communications satellites launched in India have hitherto been propelled by Arianespace or Russian rockets, and the GSLV-D1 is planned as a less costly alternative.
- 22 April – The U.S.-based current affairs magazine TIME apologizes emphatically for the offense caused by the printing of a depiction of Muhammad – considered a blasphemy in Islam – which had sparked large riots in Kashmir the previous day.
- 22 April – The government is outraged when medical reports suggest that many of the 16 soldiers killed by Bangladeshi forces in border skirmishes were mutilated and tortured before being murdered.
May, 2001
- 1 May – The number of Tibetan children under the age of 13 crossing the Himalayas to enter India doubled to 1,500 in the first four months of the year according to the Reception Centre for Tibetan Refugees.
- Early May – Ten people are killed in pre-electoral clashes in the northeastern state of Assam as the outlawed separatist United Liberation Front of Asom (ULFA) clashes with soldiers. State elections are to be held on 10 May.
- Early May – Parliamentary Affairs Minister Pramod Mahajan announces that the government will open up the country’s arms production industry to private investors, including up to 26% to foreign capital.
- Mid-May – The ruling BJP suffers defeat in five key state elections, losing ground to the opposition Congress (I) party in Assam, Kerala, and Pondicherry. In Tamil Nadu a coalition allied to Congress (I) sweeps to power making Jayaram Jayalalitha, a former film star with a conviction for bribery, chief minister there. In West Bengal the communist Left Front is returned to power continuing its record as the world’s longest serving elected communist government.
- Mid-May – Prime Minister Vajpayee announces that India will honour the ASEAN treaty keeping Southeast Asia a nuclear weapons-free zone.
- Mid-May – Tarun Gogoi, the new Congress (I) chief minister of Assam, declares that he will press for a ceasefire with separatist rebels, but he faces opposition from the BJP-controlled federal government.
- Mid-May – Indian troops cooperate with their Myanmar counterparts in a joint offensive along their common border. Rebels from Nagaland, Manipur, and Assam are targeted.
- 24 May – The government extends an offer of talks on Kashmir to Pakistani ruler General Pervez Musharraf but ends India’s six-month unilateral ceasefire in the disputed region.
June, 2001
- 2 June – The federal government imposes direct rule in the northeastern state of Manipur after the state government collapsed.
- Early June – Foreign Minister Jaswant Singh signs a defense deal with Russia worth a potential $10 billion including plans to establish an air-defense system to cover the entire country and several projects to develop new aircraft.
- 6 June – Police intercept an illegal consignment of 85 human skulls near the border with eastern Nepal. The heads were apparently en route to the lucrative tourist trade in the Himalayan country and are believed to have been raided, some fairly recently, from Christian graveyards in northeast India. No smugglers are caught.
- 10 June – The Kashmiri separatist All Party Hurriyat Conference announces the suspension of all strikes and rallies in the province pending a summit between Indian and Pakistani leaders scheduled for July.
- 15 June – A plot to bomb the United States embassy in New Delhi, allegedly masterminded by the notorious Osama bin Laden, is foiled by police.
- 17 June – Thousands of demonstrators clash with police and set fire to the Manipur state legislature in Imphal. The protests are over an agreement between the government and separatist rebels from the neighbouring state of Nagaland to extend their three-year ceasefire for another year, and to widen the deal to areas beyond the state. The protestors claim that the extension will undermine regional security.
- 18 June – The government announces that Pakistani military ruler General Pervez Musharraf is expected in India on 14 July for a landmark summit with Indian leaders.
- 21 June – A deal is signed by which the world-famous Taj Mahal monument is to receive private sponsorship from the Taj Hotel Group.
- 22 June – At least 64 people die when a train plunges off a bridge in Kerala state. The following day 50 people drown in West Bengal when an overcrowded boat capsizes on the Ganges River.
Comments: The Ascendant of the eclipse chart is Pisces and it’s the 11th house of the India chart. The eclipse falls in the 4th house of natural calamities in the eclipse chart. A dire natural malefic Mars, is in exact degree to the degree of the eclipse, thereby increasing the maleficiency. Since, the events listed are many, in a nutshell, we witnessed major earthquake in Gujarat, floods, strikes in telecom sector (Gemini sign), accidents in airline sector (eclipse in Gemini, along with Mars in close degrees), etc. The lord of the 4th house (signifying natural calamities) of the eclipse chart, Mercury is also afflicted by being in conjunction with the eclipse and its also Rx.
June 21, 2001, 5.27.45 pm, Total Solar eclipse. Not visible in India.


The events during the period 2001/2002 are as follows: (source-Wikipedia).
June, 2001
- 2 June – The federal government imposes direct rule in the northeastern state of Manipur after the state government collapsed.
- Early June – Foreign Minister Jaswant Singh signs a defense deal with Russia worth a potential $10 billion including plans to establish an air-defense system to cover the entire country and several projects to develop new aircraft.
- 6 June – Police intercept an illegal consignment of 85 human skulls near the border with eastern Nepal. The heads were apparently en route to the lucrative tourist trade in the Himalayan country and are believed to have been raided, some fairly recently, from Christian graveyards in northeast India. No smugglers are caught.
- 10 June – The Kashmiri separatist All Party Hurriyat Conference announces the suspension of all strikes and rallies in the province pending a summit between Indian and Pakistani leaders scheduled for July.
- 15 June – A plot to bomb the United States embassy in New Delhi, allegedly masterminded by the notorious Osama bin Laden, is foiled by police.
- 17 June – Thousands of demonstrators clash with police and set fire to the Manipur state legislature in Imphal. The protests are over an agreement between the government and separatist rebels from the neighbouring state of Nagaland to extend their three-year ceasefire for another year, and to widen the deal to areas beyond the state. The protestors claim that the extension will undermine regional security.
- 18 June – The government announces that Pakistani military ruler General Pervez Musharraf is expected in India on 14 July for a landmark summit with Indian leaders.
- 21 June – A deal is signed by which the world-famous Taj Mahal monument is to receive private sponsorship from the Taj Hotel Group.
- 22 June – At least 64 people die when a train plunges off a bridge in Kerala state. The following day 50 people drown in West Bengal when an overcrowded boat capsizes on the Ganges River.
July, 2001
- Early July – Police in the southern state of Tamil Nadu are ordered to shoot violent protestors on sight following unrest in the region prompted by the brief detention of the state’s former chief minister Muthuvel Karunanidhi. The arrest was ordered by new chief minister Jayaram Jayalalitha, an arch-rival of Karunanidhi.
- 4 July – The country’s first ever private FM radio station – Radio City – is launched in Bangalore.
- Early July – Archaeologists announce the discovery of possibly the world’s second-largest Buddhist stupa (a holy domed building containing relics or artifacts associated with Buddha) in Bihar. It is believed to date from the 6th century.
- 5 July – Thousands of women clash with police in Imphal, Manipur, in protest at the federal government’s negotiations with neighbouring Naga rebels. The rally deliberately contravenes a curfew imposed in the city after riots in June.
- Early July – The transport ministry announces plans ahead of the India-Pakistan summit to open links with Pakistan, including across the Line of Control in Kashmir.
- First half of July – 500,000 people are displaced by severe flooding in the eastern state of Orissa.
- 13 July – Shabir Shah, the leader of the Jammu and Kashmir Democratic Party (JKDP), is arrested ahead of the landmark India-Pakistan summit in Agra.
- 17 July – Hopes for a new era in Indo-Pakistani relations are disappointed when the summit between Prime Minister Vajpayee and newly appointed Pakistani president Pervez Musharraf fails to make progress on the Kashmir issue and ends without agreement.
- 23 July – 30,000 people clash with police again in Imphal in continuing protests against the government’s peace proposals with neighbouring Naga rebels.
- 25 July – Famed Bandit Queen turned M.P. Phoolan Devi is assassinated by masked gunman at the gate of her New Delhi residence at the age of 37.
- Late July – Prime Minister Vajpayee accepts the invitation from Pakistani President Musharraf to travel to Pakistan for a second round of bilateral talks. However, his acceptance comes amid reports that he has privately derided Musharraf’s diplomatic skills.
- 31 July – The ruling BJP orders Prime Minister Vajpayee to remain in office, rejecting his offer to resign. Vajpayee cited difficulties in maintaining a workable coalition in government.
August, 2001
- 9 August – The security status of four districts of Jammu is changed, so that now all six districts of Jammu as well as all six districts of the Kashmir valley are designated “disturbed areas”, leaving Ladakh as the only part of Jammu and Kashmir not covered by the Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act of 1990.
September, 2001
- Early September – India’s first police office dedicated specifically to Internet crimes opens in Bangalore.
- 21 September – Jayaram Jayalalitha, the controversial former film star, is forced to resign as chief minister of Tamil Nadu after the Supreme Court ruled her appointment was invalid due to her conviction for corruption.
- 23 September – Three-year-old U.S.-led economic sanctions against India’s external defense trade are lifted as part of the U.S. attempt to bolster its regional alliances against Islamic militants. The sanctions were imposed on India and Pakistan in 1998 after they both conducted nuclear weapons tests.
- Late September – 10,000 soldiers are deployed along the border with Nepal in an effort to combat the flow of militants and criminals who are thought to use southern Nepal as a base for operations in India.
- 30 September – Madhavrao Scindia, the deputy leader of the opposition Congress (I) party, is one of eight people killed in a plane crash.
October, 2001
- 1 October – 38 people are killed in a concerted attack on Indian government buildings in Srinagar, Kashmir. A Pakistani suicide bomber from the Jaish-e-Mohammad (Army of Mohammad) detonates a government jeep packed with explosives at the entrance of the buildings, while troops disguised as policemen enter the complex and begin firing. The All-Party Hurriyat Conference of Muslim separatists and the Pakistani government both immediately condemn the attack but the Indian government accuses the Pakistani authorities of collusion.
- 2 October – Keshubhai Patel resigns his position as chief minister of Gujarat following the poor showing of his BJP in elections there. He is replaced by the BJP’s general secretary, Narendra Modi.
- 2 October – U.S. Secretary of State Colin Powell suggests that Muslim Kashmiri separatists in India will be targets in the “war on terrorism”.
- 7 October – Narendra Modi is sworn in as the chief minister of Gujarat.
- 8 October – Despite increased tensions after attacks in Kashmir, Prime Minister Vajpayee and Pakistani President Musharraf agree to cooperate against international terrorism in a rare telephone conversation.
- 12 October – The U.S. freezes the assets of the Pakistani-based Kashmiri separatist group Jaish-e-Mohammad as one of its targeted terrorist groups.
- 15 October – The disgraced former defence minister George Fernandes is reappointed to his post. He left the cabinet in March over a prominent corruption scandal.
- 16 October – Despite pressure from the U.S. to renew negotiations over Kashmir, the government insists that it will continue to repel incursions into Indian-administered Kashmir by rebels it says are backed by Pakistan. Indian forces began shelling positions on the Pakistani side of the Line of Control the previous day.
- 22 October – Interest rates are cut to their lowest level since 1973, falling by half a percentage point to 6.5%.
- 24 October – President K.R. Narayanan signs into law the Prevention of Terrorism Ordinance granting extra powers to the police in an effort to combat terrorism. As well as allowing the detention of suspected terrorists for up to three months without charge, the decree makes it a duty for people to report suspicious behavior.
- 26 October – Japan becomes the latest country to lift economic sanctions imposed on India and Pakistan after both countries conducted nuclear tests in 1998.
November, 2001
- 1 November – The government accuses neighbouring Pakistan of provocation, saying it has been slowly increasing its military presence in Kashmir.
- 4 November – Hundreds of thousands of lower caste Hindus convert to Buddhism in one of the largest mass conversions in recent years.
- 6 November – Around 15,000 labourers, peasants, women, and lower caste Hindus demonstrate in New Delhi against the government’s cooperation with international financial institutions, which they claim is self-destructive.
- 12 November – A strike called by groups opposed to a plan for greater representation for the ethnic Bodo people brings the state of Assam to a standstill. India’s central government has proposed creating Bodo councils in regions where they form a majority of the population, but non-Bodos have raised fears that they will become the targets for racial discrimination at the hands of the new councils.
December, 2001
- 7 December – The government of the state of Meghalaya is toppled by a vote of no confidence. The United Democratic Party will be replaced by an opposition coalition called the People’s Forum of Meghalaya.
- 13 December – Six gunmen injure 22 people and kill six police officers before they themselves are killed in a dramatic “suicide” attack on the central parliament buildings in New Delhi. No members of the government are hurt. The government blames the attack on two Pakistan-based Kashmiri militant groups, Jaish-e-Mohammad and Lashkar-e-Toiba, the former of which had also attacked the local government centre in Indian-administered Kashmir in October.
- Early December – The economy shows signs of a rapid slowdown as inflation strikes a 20-year low of 2.27% at the beginning of the month, falling from a 10-year high of 8.57% in February.
- Mid-December – Tension between India and Pakistan escalates rapidly after the Indian government accuses its Pakistani counterpart of supporting a terrorist attack on the Indian parliament in New Delhi. The threat of all-out war between India and Pakistan looms large across the New Year with both sides massing forces along their common border. There is an exchange of mortar fire across the “line of control”, the de facto border in Kashmir, on 2 January. However, the leaders of both countries express hope that conflict could be avoided amid a massive international diplomatic effort, including a regional visit from UK Prime Minister Tony Blair. Some of the heat is released when the leadership of the groups believed to have been involved in the parliamentary attack are arrested in Pakistan and Indian Prime Minister Vajpayee announces that war is “unnecessary”.
January, 2002
- 9 January – The government announces that it is laying landmines along the entire length of its 2,800-km border with Pakistan.
- 10 January – 800 protesters are arrested in a large-scale illegal protest against the Communist government of West Bengal, which brings the state to a standstill. The authorities there had outlawed “disruptive” protests at the end of 2001.
- Mid-January – Direct flights to China are set to resume for the first time in 40 years after diplomatic talks between the two countries.
- 16 January – Archaeologists announce the discovery of ancient man-made structures off the Gujarati coast which could be as many as 9,500 years old – 5,500 years older than the ancient Harappan civilisation whose remains are found around the same region.
- 22 January – Five policemen are killed and 20 other people injured when Islamic militants attack an American cultural centre in Kolkata. Police arrest at least 50 suspects in the wake of the incident. The government immediately accuses its Pakistani counterpart of involvement in the attack.
- Late January – The government is roundly criticised for testing a short-range version of its Agni ballistic missile on 25 January, the day before the country’s Republic Day, at a time when military tensions with Pakistan remain high.
February, 2002
- 3 February – Russia gives its full backing to India over the Kashmir dispute with neighbouring Pakistan.
- Mid-February – The Cellular Operators Association announces that the ownership of mobile phones in India rocketed by 75% in the previous year. Almost 6 million Indians now own mobile phones.
- 24 February – The Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) loses control of state governments in Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, and Uttaranchal (now known as Uttarakhand) according to election results released this day. The BJP is expected to retain a role in a coalition in Uttar Pradesh (the most populous state in India), whereas the Punjab and Uttaranchal state legislatures are now dominated by the opposition Congress party.
- 27 February – One of the worst pogrom unleashed against a community after 59 pilgrims killed aboard a fire in a train in Godhra.
- 28 February – Violence against a community in the Gujarati city of Ahmadabad leaves over 500 dead. The violence came after the death the previous day of 58 who died in Godhra, near Vadodara (the exact circumstances remain unclear). Those victims were said to be supporters of the Hindu group Vishwa Hindu Parishad (VHP), who had been travelling from the Ayodhya region, near the border with Nepal. VHP has been campaigning for the construction of Ram temple in the Ayodhya site following the destruction of an ancient mosque there in 1992. Violence rages on through March, claiming hundreds of lives. (See also 2002 Gujarat violence.)
- 28 February – Gulbarg Society massacre: During the 2002 Gujarat riots, a mob attacked the Gulbarag Society, a lower middle-class neighbourhood in Chamanpura, Ahmedabad. Most of the houses were burnt, and at least 35 victims including a former Congress Member of Parliament Ehsan Jafri, were burnt alive, while 31 others went missing after the incident, later presumed dead, bringing the total of the dead to 69.
- 28 February – Finance Minister Yashwant Sinha presents the 2002–03 budget. Amongst its major features are a 4.8% increase in defence spending and a 5% surcharge on income tax to pay for this.
March, 2002
- 1 March – Continuing violence in Ahmedabad kills 28; police shoot and kill 5 rioters.
- 2 March – J. Jayalalithaa returns to power in Tamil Nadu as chief minister. In December 2001, an appeals court had quashed her October 2000 corruption conviction that disqualified her from standing for election.
- 3 March – The speaker of the Lok Sabha, Ganti Mohana Chandra Balayogi, is killed in a helicopter crash in the southern state of Andhra Pradesh. He was the first low-caste Dalit to be elected to the post.
- 6 March – Novelist Arundhati Roy, a high-profile campaigner against the Narmada river dams project, is sentenced by the Supreme Court to one day in prison for contempt of court because of an affidavit she had written criticising the court.
- 8 March – President’s rule is imposed on the northern state of Uttar Pradesh as no party could command a majority after the recent elections.
- 15 March – 9,000 suspected Hindu hardliners are arrested, including 8,000 in Mumbai alone, in a massive crackdown aimed at preventing further interreligious violence. Tensions are high surrounding attempts to construct a new Hindu temple on the site of the Ayodhya mosque, which was destroyed by Hindu extremists in 1992.
- 15 March – The New Delhi High Court overturns the October 2000 corruption conviction of former prime minister P.V. Narasimha Rao.
- 25 March – Police arrest Yasin Malik, leader of the separatist Jammu and Kashmir Liberation Front (JKLF), in Srinagar.
- 26 March – The government pushes through its controversial Prevention of Terrorism Ordinance (POTO) bill in a rare joint session of both houses of parliament, only the third since independence. In separate sessions, the Lok Sabha had passed the bill on 18 March but it was defeated in the Rajya Sabha on 21 March.
April, 2002
- 4 April – On his first visit to Gujarat since the violence there began, (See 2002 Gujarat violence) Prime Minister Vajpayee makes an impassioned speech appealing to the Hindu and Muslim communities to end the violence, saying that the “shameful events” in Gujarat are a “blot” on India.
- 16 April – Up to 10 million public sector workers, including 32,000 employees of state-owned banks, hold a one-day strike against government privatisation plans.
- 18 April – India signs a deal to buy a $146 million weapon-seeking radar system built by the U.S. company Raytheon. It is the first significant U.S. arms sale to India for a decade.
- 29 April – Minister for Coal and Mines Ram Vilas Paswan resigns on the issue of the Gujarat violence, which he says has “tarnished India’s image” while the government’s role appears to be that of a “silent spectator”. He pulls his Lok Janshakti Party out of the ruling National Democratic Alliance coalition.
May, 2002
- 3 May – The stalemate in Uttar Pradesh is resolved when Mayawati of the Bahujan Samaj Party is sworn in as chief minister, in a coalition with the BJP.
- 10 May – Manohar Joshi of the Shiv Sena party is elected speaker of the Lok Sabha.
- 14 May – An attack by militants on an army base in Kashmir, in which 34 people are killed, leads to sharply rising tensions with Pakistan. On 15 May, Vajpayee says in the Lok Sabha: “We will have to retaliate.” Fears increase that the situation might escalate into a nuclear exchange.
- 21 May – Moderate Kashmiri separatist leader Abdul Ghani Lone is assassinated. On the same day Vajpayee begins a five-day visit to Kashmir. In a martial speech on 22 May, he says that “a new chapter of victory and triumph will be written in the history books soon”.
- 23 May – Indian paratroops complete a two-week exercise with U.S. forces south of New Delhi.
- 31 May – Both the UK Foreign and Commonwealth Office and the U.S. State Department issue unprecedented advice to their citizens living in India to leave the country.
- 2002 heatwave in India
June, 2002
- June – Tensions between India and Pakistan are reduced largely as a result of international pressure. Pakistani President Pervez Musharraf assures visiting U.S. Deputy Secretary of State Richard Armitage that the cessation of cross-border infiltration will be made “permanent” and “irreversible”. On 20 June, Indian Defense Minister George Fernandes says that infiltration has “nearly ended”. Analysts note, however, that some 3,000 indigenous and Pakistani militants are already inside Indian-controlled Kashmir, and violent incidents continue on a daily basis. On 9 June police in Srinagar arrest Syed Ali Shah Geelani, leader of the hardline Islamist Jamaat-i-Islami party and a prominent leader of the All Parties Hurriyat Conference.
- 22 June – Ashok Singhal, leader of the Vishwa Hindu Parishad (VHP), announces that the VHP is no longer bound by its earlier promise to the government to await a court ruling before embarking on the construction of a temple to the god Rama on the site of the destroyed Babri mosque at Ayodhya.
Comments: The Ascendant rising in the eclipse chart is Scorpio, which is the 7th house of the India chart. The eclipse is in the 8th house of the eclipse chart. The 8th house as said earlier is all mass happenings. There is no doubt that Jupiter is giving its protective cover to the eclipse in Gemini. But, a strong Mars Rx is also aspecting the eclipse in Gemini by the 8th aspect, which is very dangerous. Mars being strong in the 7th house of India chart, gave violence, fear of war, riots, etc. The lord of the 10th house (Government) of the eclipse chart is Sun. The Sun is in eclipsed in the 8th house and aspected by strong Mars, which gave several States witnessing CMs resigning and taking over, Government toppling, etc.
July 12, 2010, 1.10.27 am, Total Solar Eclipse. Not visible in India.


The events during the period 2010/2011 are as follows: (source-Wikipedia).
June. 2010
- 2 June – 2010 Indian heatwave: A heat wave strikes India and South Asia, reaching 53°C (127°F) and killing many hundreds of people.
- 7 June – The Magistrate court in Bhopal, India convicts eight people, one posthumously, for their role in the Bhopal disaster industrial castastrophe 25 years ago in 1984.
- 17 June – Heavy rains claim 46 lives in Maharashtra.
- 23 June – 1 person is killed when a crane crashes at Chennai International Airport, Chennai.
- 25 June – 17 people are killed and 25 others injured when an overcrowded bus collided head-on with a speeding truck near Chenaki More, about 30 km from Patna, India.
- 26 June – Four people are killed and five wounded in violence in Indian-administered Kashmir’s Sopore area.
- 29 June – 2010 Maoist attack in Narayanpur: At least 26 policemen are killed in a Maoist attack in the central Indian state of Chhattisgarh.
July, 2010
- 5 July – A nationwide strike takes place in India in protest at a recent rise in fuel prices.
- 8 July – A bomb rips through the engine and coach of a passenger train in Assam, killing one person.
- 13 July – One death and three injuries result from a stampede during pulling of Ratha Yatra chariots in Puri, India.
- 13 July – The Supreme Court of India tentatively approves the Tamil Nadu government’s new quota law, providing 69% of employment in educational institutions to scheduled castes and tribes and other backward classes.
- 14 July – Senior Indian Army officer Major AK Thinge is killed in battle in Kashmir.
- 19 July – Two trains collide in the Birbhum district of West Bengal with at least 50 people feared dead.
- 20 July – Former Indian junior diplomat Madhuri Gupta is charged under the Official Secrets Act with spying for Pakistan.
- 21 July – Unidentified gunmen on motorcycles fatally shoot Indian civil rights campaigner and environmentalist Amit Jethwa in Ahmedabad, Gujarat.
- 23 July – The Indian Government unveils a solar power touch-screen laptop, cheaper than America’s iPad, expected to be on sale next year.
August, 2010
- 1 August – Six people die in the Indian province of Jammu and Kashmir after a third day of clashes between security forces and Kashmiri separatists.
- 4 August – About 70 Indian police personnel are reported missing in Chhattisgarh forests amid a major engagement with Maoist guerrillas; they are later found. No casualties have been reported.
- 6 August – 2010 Leh floods: Flash floods in the Ladakh region of India’s Jammu and Kashmir state kill at least 113 people and leave lots of others missing.
- 7 August – 2010 Mumbai oil spill: An oil spill stretching at least two miles long occurs in the Arabian Sea offshore Mumbai, India, after a vessel from Panama collides with another vessel from St. Kitts. The Panamanian ship was carrying 2,662 tons of oil, 283 tons of diesel and 88,040 liters of lube oil when it became grounded and started to leak.
- 12 August – India issues the producer of the controversial BlackBerry devices a 31 August deadline to give the Indian Government access to its services or be shut down over concerns the devices could be used to commit a repeat of the 2008 Mumbai attacks.
- 15 August – India celebrated its 63rd Independence Day. Sreeram Chandra from Andhra Pradesh won the Indian Idol Season 5 music reality show beating Bhoomi Trivedi and Rakesh Maini.
- 18 August – A school building collapses due to heavy rain in the village of Sumgarh in the Indian state of Uttarakhand, killing at least 17 schoolchildren.
- 27 August – Police in India kill Umakanta Mahato, a top Maoist guerrilla wanted in connection with the Gyaneshwari Express train derailment in May.
September, 2010
- 10 September – Thousands of people are evacuated in Delhi over flooding fears.
- 20 September – At least 21 people are killed and dozens are injured after 2 trains collide in the Shivpuri district of India’s Madhya Pradesh state.
- 23 September – Speeding train kills 7 elephants in Eastern India.
- 29 September – India launches a national identity scheme aimed at reducing fraud and improving access to state benefits.
October, 2010
- 3 October – XIX Commonwealth Games, were held in Delhi, India, from 3 to 14 October 2010.
- 3 October – Violet Line of the Delhi Metro system opened.
- 10 October – At least 36 people die after an overloaded boat capsizes on the Ganges River in the Buxar district of India’s Bihar state.
- Mid-October, Mrs. Kashmira and Dr. Leo Rebello visit Andaman Islands, flying directly from Bombay to Portblair, on a chartered flight of Yatra travel, and find Jarawas (tar black people) still roaming fully naked hardly 30 km away from the Governor’s Palace. Visit the Cellular Jail and recommend that the said imposing edifice should be turned into a Heritage-Jail Hotel, and oppose the setting up of an Allopathy hospital on the campus of the Cellular Jail to medicate the Jarawas, destroying their original genetic pool of over 5000 years old.
- 11 October – 18 people are killed when a bus falls into a river in Bulandshahr district, Uttar Pradesh, India.
- 25 October – More than 700 species of ancient insects are discovered preserved in amber in an ancient rainforest in India.
- 30 October – At least 16 people drown and 70 are missing after an overcrowded ferry sinks in a river in West Bengal, eastern India.
November, 2010
- 1 November – At least 74 people drown after a ferry-boat capsizes on the Muri Ganga River in West Bengal, India.
- 2 November – 17 people are killed and three others injured when a truck carrying them overturned at Tarapur talukav near Indranaj in India. The truck was on its way from Surat to Bhavnagar.
- 15 November – 66 people die after a building collapses in eastern New Delhi.
- 21 November – Seven people are killed after a bomb planted by suspected Maoist rebels explodes in Aurangabad district, Bihar, northeastern India.
December, 2010
- 5 December – 20-year-old Nicole Faria from Bangalore, Miss India, wins the Miss Earth 2010 crown in Vinpearl Land, Nha Trang, Vietnam.
- 10 December – Agni-II plus missile test fails in Orissa, India test-fired an upgraded version of the Agni-II plus nuclear-capable intermediate range ballistic missile off the Orissa coast. The test was declared a failure. The latest version of the “Agni” series missile is described as a two-stage, solid propellant rail and road mobile missile.
- 26 December – A collision between a bus and a mini-truck kills 34 people and leaves 30 injured, near the town of Budaun in Uttar Pradesh state, in northern India.
- Late December – Onion price rise in Indian markets leads to political tensions.
January, 2011
- Union Home Ministry wound up the Srikrishna committee on Telangana following submission of its report.
- Arabinda Rajkhowa, chairman of ULFA, was released on bail from the Guwahati central prison.
- India and Pakistan exchange the annual lists of their nuclear installations and facilities under the Agreement on the Prohibition of Attack against Nuclear Installations, which was signed on 31 December 1988.
- Nagesh Pydah assumed charge as Chairman and Managing Director of the Oriental Bank of Commerce.
- Yashwant Sonawane, Additional District Collector of Malegaon burnt alive by oil mafia at Manmad near Nashik (Maharashtra).
- 102 lives lost in stampede at Sabarimala Shrine (Kerala).
- Eminent classical singer Bhimsen Joshi passes away at the age of 88.
- Karnataka Governor sanctions prosecution of CM B.S.Yeddyurappa.
- Suresh Kalmadi sacked as Chairman of Commonwealth Games Organizing Committee.
February, 2011
- Former Telecom Minister A.Raja sent to Tihar Jail in 2G spectrum case.
- Bombay High Court upholds death penalty for Ajmal Kasab.
- Ahmedabad court convicts 31, acquits 63 in Godhra train burning case.
- 34th National Games Held in Ranchi, Jharkhand.
- Kidnapped Malkangiri Collector released by Maoists.
March, 2011
- Supreme Court strikes down CVC PJ Thomas’ appointment.
- PM Manmohan Singh and PM Gilani of Pakistan engage in cricket diplomacy on the occasion of India-Pakistan semi final match in Cricket World Cup 2011.
- Supreme Court dismisses Aruna Shanbaug’s euthanasia plea.
- Hasan Ali remanded to judicial custody.
- Saina Nehwal clinches Swiss Open Grand Prix.
- DGCA revokes licenses of 14 fake pilots.
- Census 2011 shows increase of 181 million in total population.
- 2011 I-League 2nd Division begins.
April, 2011
- 2 April – India beat Sri Lanka and wins the 2011 Cricket World Cup.
- Dorjee Khandu, Chief Minister of Arunachal Pradesh since 2007, dies in a helicopter crash.
- Anna Hazare undertakes fast for Jan Lokpal Bill at Jantar Mantar, New Delhi.
- Supreme Court grants bail to civil rights activist Binayak Sen.
- Visit of Prime Minister Abhisit Vejjajiva of Thailand to India.
- Five corporate honchos (Sanjay Chandra of Unitech; Gautam Doshi, Surender Pipara and Hari Nair of Reliance ADAG; Vinod Goenka of Swan Telecom) arrested in 2G spectrum case.
- 2011 I-League 2nd Division ends.
May, 2011
- Mamata Banerjee sworn in as the first woman and 11th Chief Minister of West Bengal.
- Prime Minister Manmohan Singh announces aid of ₹ 225 billion for African countries to develop infrastructure facilities on the eve of IInd Indo-Africa summit.
- J.Jayalalitha, Oommen Chandy, Tarun Gogoi and N. Rangaswamy takes over as Chief Ministers of Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Assam and Puducherry respectively, as a result of assembly elections.
- Supreme Court quashes Karnataka Speaker’s decision to disqualify 16 MLA’s.
- German Chancellor Angela Merkel conferred Jawaharlal Nehru Award for International Understanding for 2009 by President Pratibha Patil.
- India ratifies UN protocol against human trafficking.[27]
- 2010–11 I-League: Salgaocar FC won the title by beating JCT FC 2-0 in the final match of the season.
- 2011 Santosh Trophy
June, 2011
- Senior journalist and investigations editor with English newspaper ‘MiD DAY’, J. Dey, is shot dead in Mumbai.
- Election Commission of India launches the IIDEM (India International Institute of Democracy and Election Management).
- Famous painter M.F Hussain passes away.
- New Zealand Prime Minister John Key visits India.
- India gets first e-waste management rules.[33]
- India ranks 123rd on the global environment index.
- Supreme Court appoints committee to examine the secret chambers of Sri Padmanabhaswamy Temple, Kerala.
Comments: The Ascendant rising in the eclipse chart is Aries, which is the 12th house of India chart. The 12th house signifies losses among all the other things. The degree of Mars is in exact degree with the eclipse degree, which results into degreecal conjunction. The eclipse happens in the 3rd house of the eclipse chart. There are many events those have been listed above. To summarise, due to Mars degreecal closeness to eclipse degree, several events of accident in communication sectors have occurred (Gemini rising and Mars in Leo a fiery sign in the same degree to eclipse point). Events like Mumbai oil spill, testing of Agni missile, inauguration of Metro in Delhi are all related to communication sectors. If you consider India chart, the eclipse is occurring in the 2nd house, Mars is in the 4th house of natural calamities, Saturn in the 6th house of protests (from the eclipse chart), etc. This has given the beginning of the IAC movement by Anna Hazare which has given a new change in the political system. The eclipse is also in the Rahu/Ketu axis (though not close degreecally), giving more maleficiency.
July 1, 2011, 2.23.54 pm, Partial Solar Eclipse. Not visible in India.


The events during the period 2011/2012 are as follows: (source-Wikipedia).
July, 2011
- 26 killed in a series of bomb-blasts in Mumbai.
- Gorkhaland Territorial Administration (GTA) agreement signed.
- India-Bangladesh ink border management deal.
- 18 July – India’s 25th nuclear power plant being built at Rawatbhata, Rajasthan.
- Newly formed National Green Tribunal (NGT) conducts its first sitting.
August, 2011
- Reserve Bank of India issues draft guidelines for new bank licences.
- Nation celebrates Independence Day on 15 August.
- Parliament passes sense of the house resolution on Lokpal bill.
- Sustainable Competitiveness Report 2011 presented, Delhi is first.
September, 2011
- 6.8 earthquake in Sikkim, tremors across India on 18 September.
- Land Acquisition, Rehabilitation and Resettlement Bill, 2011 presented in lok sabha.
- PM Manmohan Singh visits Dhaka on a landmark visit.
- 2011 Durand Cup
- 2011 Indian Federation Cup
- Bhanwari Devi murder case
October, 2011
- F1 2011 Race comes to India at the Buddh International Circuit, Noida.
- 7 billionth baby born on 31 October 2011, Nargis in Uttar Pradesh.
- Saving Bank Interest rate decontrolled by RBI.
- National Manufacturing Policy cleared by Cabinet.
- Planning Commission releases the second India Human Development Report (HDR) 2011.
- President of Afghanistan, Hamid Karzai, visits India.
- Chhattisgarh police superintendent Ankit Garg is accused of the torture of schoolteacher and alleged Naxalite Soni Sori.
November, 2011
- Maoist leader Kishenji killed in encounter in West Bengal.
- Companies Bill and Pension Bill cleared by Cabinet.
- Indian representative elected to head the Joint Inspection Unit, the UN’s only external oversight body.
- India ranks 134th on UN Human Development Index.
- Longest rail (4286 km) of India, Vivek Express, is flagged off.
- Sonia Gandhi (11th) and Manmohan Singh (19th) figures among the top 20 most powerful people on earth in the Forbes list.
December, 2011
- More than 50 killed in fire accident at AMRI hospital, Kolkata.
- 150 perish in West Bengal hooch tragedy.
- Court directs 21 social networking websites to take off offensive content.
- Lok Sabha passes Lokpal Bill, Hazare cancels fast due to lukewarm response at Mumbai.
- Cyclone Thane claims 33 lives in Tamil Nadu and Puducherry.
January, 2012
- 3 January: President inaugurates new SHAR Mission Control Centre.
- 9 January: 10th Pravasi Bharatiya Divas kicks off in Jaipur. Chief guest – Kamla Persad-Bissessar, Prime Minister of Trinidad and Tobago.
- 11 January: 42% of Indian children are malnourished – Hunger and Malnutrition (Hungama) report.
- 13 January: 5 million students perform Surya namaskar in Madhya Pradesh.
- 19 January: Delhi High Court grants bail for Suresh Kalmadi in Commonwealth Games Scam.
- 26 January: Nation displays military might on 63rd Republic Day; Thailand Prime Minister Yingluck Shinawatra, chief guest of India’s 63rd Republic Day celebrations.
February, 2012
- 2 February: Supreme Court cancels all 122 licences given by A Raja in 2G spectrum case.
- 5 February: Special CBI court dismisses Subramanian Swamy’s petition to prosecute Home Minister P.Chidambaram in 2G spectrum case.
- 8 February: Three Bharatiya Janata Party ministers caught watching objectionable video clip in Karnataka Assembly, Resign.
- 11 February: Army Chief V.K. Singh withdraws petition from Supreme Court in age-controversy.; Advanced Interceptor missile is successfully test-fired.
- 14 February: Blast at an Israeli embassy car in Delhi.
- 16 February: Two fishermen, mistaken for pirates, shot dead off Kerala coast by Italian ship.
- 20 February: Six killed in stampede at Bhavnath temple in Junagadh district, Gujarat.
March, 2012
- 3 March: State Assembly election process comes to an end in Uttar Pradesh and Goa.
- 6 March: Election results for five state assemblies are announced; Samajwadi Party (Uttar Pradesh), Bhartiya Janata Party (Goa), Indian National Congress (Manipur & Uttarakhand), Shiromani Akali Dal-BJP combine (Punjab) emerge winners.
- 14 March: Irom Sharmila fast against AFSPA goes on for 11 years. Indian Rail Budget 2012–13 presented by Rail Minister Dinesh Trivedi.
- 16 March: Union Budget for 2012–13 is presented by Finance Minister Pranab Mukherjee.
- 18 March: Dinesh Trivedi steps down as Railways Minister after pressure from TMC.
- 21 March: Soumitra Chatterjee selected for Dadasaheb Phalke award for 2011.
- 22 March: India votes against Sri Lanka on the resolution to ‘credibly investigate’ allegations of violations during the war against Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam in 2009 in the United Nations Human Rights Council.
- 29 March: India hosts 4th BRICS summit at New Delhi. Heads of state of Brazil, Russia, China and South Africa are hosted by India.
April, 2012
- 8 April: Pakistan President Asif Ali Zardari visits India on a personal visit to Ajmer Sharif.
- 11 April: A pair of great earthquakes occur in the Wharton Basin west of Sumatra in Indonesia. The maximum Mercalli intensity of this strike-slip doublet earthquake was VII (Very strong). Ten were killed, twelve were injured, and a non-destructive tsunami was observed on the island of Nias.
- 12 April: 18 get life term for Ode village massacre during 2002 Gujarat riots.
- 17 April: RBI cuts repo rate by 50 basis points for the first time in three years.
- 18 April: Major fire in the signalling system at Kurla brings Central line and Harbour line of Mumbai Suburban Railway to a standstill and two commuters lose their lives after falling off an overcrowded local train.[20] The loss was expected to be ₹170 million (US$2.4 million) to the Central Railway.
- 19 April: India successfully test fires 5000 km range Agni-V ICBM.
- 21 April: Sukma district collector Alex Paul Menon kidnapped by Maoists in Chhattisgarh.
- 24 April: Two NRI kids return to Kolkata after long legal struggle with CWS Norway.
- 26 April: Sachin Tendulkar, Rekha and Anu Aga nominated to Rajya Sabha by the President of India. Abducted BJD MLA Jhina Hikaka released by maoists after 33 days of captivity.
May, 2012
- 1 May: More than 100 feared dead after a ferry capsizes in Brahmaputra river, Assam.
- 3 May: Maoists released the Sukma Collector Alex Paul Menon after 12 days of hostage.
- 7 May: Finance Minister postpones GAAR (General Anti Avoidance Rules) implementation till 2013.
- 8 May: Over 100 Air India pilots go on strike.
- 9 May: Centre government decides to withdraw 2G review petition at the Supreme Court.
- 13 May: Indian parliament celebrates 60th anniversary.
- 15 May: A. Raja, the prime accused in 2G scam, gets bail.
- 23 May: Congress led UPA-II government completes 3 years in office.
- 27 May: Kolkata Knight Riders (KKR) win the fifth edition of the Indian Premier League
- 31 May: Bikram Singh takes over as Indian Army Chief.[36] 11th Indian Telly Awards were held.
June, 2012
- 1 June: Brahmeshwar Singh, chief of banned Ranvir Sena, is killed by unidentified assailants.
- 5 June: Sachin Tendulkar takes oath as member of Rajya Sabha.[38]
- 11 June: VS Sampath takes over as new CEC.
- 15 June:Pranab Mukherjee is UPA candidate for President of India.[40]
- 19 June: India pledges $10 bn to IMF for Eurozone.
- 22 June: Calcutta High Court strikes down Singur Land Act of Mamata Banerjee government.
- 26 June: 26/11 handler Abu Jundal is arrested by Delhi Police.
- 28 June: Surjeet Singh returns home after 30 years in Pakistan jail.
- 30 June: 19 Maoists killed in an encounter in Chhattisgarh.
July, 2012
- 4 July: Ashok Chavan named in Adarsh chargesheet.
- 6 July: Disproportionate assets case against Mayawati quashed by Supreme Court.
- 7 July: Popular Time magazine dubs Manmohan Singh as ‘underachiever’.
- 12 July: Jagadish Shettar sworn in as new Karnataka Chief Minister.
- 13 July: Panel set up by PM to review GAAR.
- 14 July: Hamid Ansari chosen as UPA nominee for vice-president.
- 20 July: Assam Violence breaks out in Kokrajhar district and adjoining areas.
- 22 July: Pranab Mukherjee is elected as India’s 13th president.
- 25 July: Pranab Mukherjee takes over the post of President of India.
- 27 July: London Olympics 2012 from 27 July to 12 Aug.
Comments: The Ascendant rising in the eclipse chart is Libra, which is the 6th house of the India chart. Both Mars and Saturn are in the same degree but in the different sign, thereby giving its malefic effects. The eclipse is happening in the 9th house of the eclipse chart. There are many events those are listed above. In a nutshell, we have seen events like violence (due to Mars’s same degree), accidents in communications sector (eclipse in sign Gemini, signifying communications and Mars’s same degree), disruptions in the railways due to fire bringing stoppage of trains in Mumbai (Gemini and Mars effect), earthquake (Mars and Ketu in the sign Taurus, which is the rising sign of India chart), etc.
July 13, 2018, 8.17.46 am, Partial Solar eclipse. Not visible in India.

The events during the period 2018/2019 are as follows: (source-Wikipedia).
June, 2018
- June 20 – Indian government report warns that 21 cities groundwater will run out by the year 2020.
August, 2018
- August 10 – August 20 – Heavy rainfall causes the 2018 Kerala floods. It was the worst flood to hit the state in a century.
- August 16 – Former prime minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee dies at 93. He was the first Indian prime minister who was not a member of the Indian National Congress party to have served a full five-year term in office.
- August 7 Muthuvel Karunanidhi (born Dakshinamurthy, 3 June 1924 – 7 August 2018) was an Indian writer and politician who served as Chief Minister of Tamil Nadu for almost two decades over five terms between 1969 and 2011. He was a long-standing leader of the Dravidian movement and ten-time president of the Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam political party. Before entering politics he worked in the Tamil film industry as a screenwriter. He has also made contributions to Tamil literature, having written stories, plays, novels, and a multiple-volume memoir. He was popularly referred to as Kalaigar, meaning artist in Tamil.
October, 2018
- 10 October – At least five people died and 30 were injured when a passenger train derailed in the north Indian state of Uttar Pradesh.
- 25 October – India Mobile Congress 2018 was inaugurated by the Minister of State (independent charge) for Communications and Minister of State for Railways, Manoj Sinha, at Aerocity, New Delhi.[25] The second edition of the iconic India Mobile Congress event saw the participation of 20 countries, 65000 visitors, 10000 delegates, 150 exhibitors, 300 international speakers and was supported by several ministries from the Government of India. The three-day event concluded on 27 October.
January, 2019
- 2 January – Government approves merger of Dena Bank and Vijaya Bank with Bank of Baroda.
- 3 January – Rajya Sabha Passes National Council for Teacher Education (Amendment) Bill.
- 4 January – Arunima Sinha becomes world’s first woman amputee to scale Mount Vinson.
- 7 January – Centre clears 10 per cent quota for economically weak in general category.
February, 2019
- 14 February – Pulwama attack: A convoy of vehicles carrying security personnel on the Jammu-Srinagar National Highway was attacked by a suicide bomber near Pulwama District, Jammu and Kashmir.
- 21 – 25 February – 2019 Assam alcohol poisonings: At least 168 people died after consuming poisonous liquor and more than 300 admitted in hospitals in Jorhat and Golaghat districts.
- 26 February – 2019 Balakot airstrike was carried out by Indian air force crossing the Line of Control directed against a terrorist training camp.
March, 2019
- 27 March – India becomes 4th nation to have Anti-satellite missile this year.
April, 2019
- 11 April – Voting for the 2019 Indian general election began
May, 2019
- 3 May – Cyclone Fani arrives on the coast of Odisha
- 23 May – Counting and declaration of results for the 2019 Indian general election. Narendra Modi secures landslide victory.
- 24 May – Surat Fire Tragedy; 22 Deaths and 17 Non-fatal injuries.
- 30 May – Narendra Modi takes oath as 14th Prime Minister of India.
Comments: The Ascendant rising in the eclipse chart is Cancer, which is the 3rd house of the India chart. The 3rd house signifies the bordering countries like China, Pakistan, etc. The Ascendant degree is close to the eclipse degree but in a different sign. So, the malefic effect of eclipse is on the Ascendant. There were basically three types of events like death of famous political leaders, tensions at the border resulting into airstrikes and terror attacks. The death of political leaders is due to the 10th lord Mars of the eclipse chart being close to Ketu. The 7th house of the eclipse chart has two malefics Mars and Ketu has given war like situation in the borders.
July 3, 2019, 12.46.05 am, Total Solar eclipse. Not visible in India.


The events during the period 2019/2020 are as follows: (source-Wikipedia).
July, 2019
- July 19 – Vidisha Baliyan becomes the first Indian to be crowned as Miss Deaf World after winning the Miss Deaf World 2019.
- July 23 – ISRO launches India’s second mission to moon chandrayaan 2
- July 30 – India bans triple talaq.
August, 2019
- August 5 – Article 370 and Article 35A revoked from Constitution of India that gives special status to Jammu and Kashmir. Government also bifurcates Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh into separate Union Territories.
- August 5 – Schools and Colleges are shut down in Pune, Mumbai, Nashik in Maharashtra due to floods.
- August 7 – Over 1.32 lakh peoples are evacuated in Sangli and Kolhapur districts of Maharashtra state due to heavy rains.
- August 16 – Millions of residents in Jammu and Kashmir still have no communication with the outside world, eleven days after the Government of India imposed restrictions on August 5. Meanwhile, 11 deaths (3 Pakistani soldiers, 6 Indian soldiers, 2 Pakistani civilians) have been reported in the Kashmir region.
- August 17 – Fire broke out in Emergency Ward of the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi. No casulties reported.
- August 22 – Former Finance minister P Chidambaram is arrested by CBI under INX media scam charges after 27 hours long drama.
September, 2019
- September 5 – Erramatti Mangamma becomes the world’s oldest living mother after giving birth to twins.
- September 6 – Chandrayaan-2, India’s second lunar partially successful. Vikram, the lander, crashes into the surface of the moon.
- September 16 — Jammu & Kashmir National Conference president Farooq Abdullah is arrested under the Public Safety Act (PSA), a law that allows detention without trial for two years.
- September 22 — U.S. president Donald Trump and Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi address 50,000 Indian Americans at the Howdy, Modi: Shared Dreams Bright Futures rally in NRG Stadium in Houston, Texas.
October, 2019
- October 24 – India and Pakistan sign a memorandum of understanding opening the Kartarpur Corridor for visa-free border crossings, allowing Indian citizens to visit the Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Sikh shrine.
- October 31 – Jammu and Kashmir (union territory) and Ladakh (union territory) will come in effect.
November, 2019
- November 9 – India’s Supreme Court rules in favor of Hindus over Ram Janmabhoomi temple.
December, 2019
- December 8 – 43 killed in Delhi’s Anaj Mandi fire, 150 officials
- December 11 – The Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2019 passed by the Parliament of India.
January, 2020
- January 27 – Agreement signed between Government of India, the Assam Government and the Bodo groups to redraw and rename the Bodoland Territorial Area District (BTAD) in Assam.
- January 30 – The 2019–20 coronavirus pandemic was confirmed to have spread to India on 30 January 2020 from China.
February, 2020
- February 8 – Polling for the Delhi Legislative Assembly elections held.
- February 11 – 2020 Delhi Legislative Assembly election’s results announced with Aam Aadmi Party securing 62 of 70 seats to claim an absolute majority in the elections.
- February 23-29 – At least 53 people are killed in communal riots in parts of Delhi.
- February 24-25 – U.S. President Donald Trump visited India for a two-day state visit, addressed a “Namaste (Welcome) Trump” event with Prime Minister Narendra Modi in Ahmedabad. Toured Mahatma Gandhi’s Sabarmati Ashram and the Taj Mahal at Agra.[3] Received a formal welcome from President Ram Nath Kovind at the Rashtrapati Bhavan Presidential Palace in New Delhi. Conducted a series of meetings with Prime minister Modi and other government officials, as well as Indian business executives.
March, 2020
- March 22 – Janta Curfew: India observed a 14-hour lockdown to prevent the spread of the Covid-19 infection.
- March 23 – Prime Minister Modi announced a 21 – day lockdown throughout India till 14 April to prevent the spread of COVID-19.
Comments: The Ascendant rising in the eclipse chart is Pisces, which is the 11th house of the India chart. The Eclipse is happening in the 4th house of the eclipse chart. The Ascendant degree, Saturn degree, Jupiter degree and Rahu/Ketu degrees are almost same. The 11th house signifies legislations passed by the Government. The rising sign of the eclipse, Pisces is aspected by Jupiter which is in the same degree. The malefic effect of Rahu/Ketu is seen on the Ascendant due to the same degree of Asc and Nodes. We have seen many important and path breaking legislations (11th house effect) passed by the Government. The outbreak of Coronovirus in mainly due to the Solar Eclipse that occurred in the month of December 26, 2019 in the sign Sagittarius. I have tweeted about its grave consequences since August 2019 in my twitter handle @jupiter_astro. If you wish, you can peruse the same. At sometime later, I will write a detailed article similar to this on all Solar eclipses those occurred in the sign Sagittarius. We also witnessed heavy rains and floods which brought lives of people to standstill. This is due to the eclipse occurring in the 4th house (natural calamities) in the eclipse chart.
June 21, 2020, 12.11.18 pm, Annular Solar eclipse. It is visible in India.

Comments: The Ascendant rising in the eclipse chart is Leo, which is the 4th house of the India chart. The rising sign of India chart being Taurus. Rahu/Ketu is in close conjunction with the eclipse degrees in Gemini. Saturn is also in the same degree as the eclipse degrees. Eclipse is having Ketu/Mars in the kendras. In the eclipse chart, the eclipse is aspected by malefic Mars. The eclipse is falling in the same degree as the natal Mars (at 7.27 degrees in Gemini) of the India chart. The 4th house signifies the natutal calamities. In the eclipse chart, the eclipse falls in the 11th house signifying slew of financial measures announced by the Government. Since, this Solar eclipse is immediately succeeding the last Solar eclipse in Decemeber 2019, its effect will be more intense. The intensity will be more also due to the closeness of Rahu to eclipse degree point and so is Saturn which is also close in the same degree. With this eclipse chart of June 21, 2020, the situation that is prevailing in India is not going to subside soon. The effect of this solar eclipse will be there atleast till next June, 2021. Moreover, its also visible in India, as can be seen from the map given above. In the eclipse chart, three major planets are conjunct in the 6th house (epidemics, riots, protests, etc), namely Saturn, Jupiter and Pluto. The sign where these planets are conjunct is Capricorn, an earthy sign. So, we will witness major earthquakes too. This will be felt mainly in the west/Northwest region of India. The 4th house (natural calamities) lord of the eclipse chart, Mars is in the 8th house (mass scale, in watery sign Pisces) and aspected by Saturn Rx. Based on this there will be floods too and heavy rainfall. The rainfall will be more of destructive nature. Apart from these, I have written few articles on Mars (http://jupiterastrology.com/c8-mundane/marss-behaviour-in-2020/), on Venus (http://jupiterastrology.com/c8-mundane/venus-and-its-relation-with-coronavirus-history-repeats-itself/) , on Ingress and June 21, 2020 eclipse (http://jupiterastrology.com/c8-mundane/effects-on-india-on-the-basis-of-aries-ingress-new-moon-charts-and-june-21st-solar-eclipse-analysis-upto-july-2020/), on Jupiter/Saturn conjunction in various signs (http://jupiterastrology.com/c8-mundane/jupiter-and-saturn-conjunction-its-effect-in-various-zodiacal-signs-a-sidereal-research/) and Saturn in Capricorn (http://jupiterastrology.com/c8-mundane/saturn-in-capricorn-sign-and-its-effects-on-india-a-statistical-analysis-by-niryana-sidereal-method/). You can read these articles as many of the events are inter-connected.
Finally, I can say that, we will not be able to get immediate relief and my fear is the current situation will be here to stay atleast for one year. We will be witnessing many negative events till such time Saturn is going to be in the sign Capricorn. For a detailed analysis on Saturn in Capricorn, read my article “Saturn in Capricorn sign and its effects on India – A statistical analysis by Niryana (Sidereal) method.”. The link is provided above.
Sundar Balakrishnan
B.Com., MFM Finance (NMIMS)
2 Year Jyotirvid and 3 Year Jyotirvisharad
(From Bharatiya Vidya Bhawan, Mumbai)
Professor of Astrology at Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan, Mumbai
Date: May 2nd, 2020
Time: 4.00 PM, Mumbai, India
(Copyright – No portion of this article can be reproduced by anyone without the written permission of the Author)
Rajiv
Pankaj